Social Security benefits were never intended to be the sole financial support during retirement but for 21% of retirees Social Security benefit is the only source of income. For most American workers, Social Security benefits are the only guaranteed retirement income that is also inflation adjusted each year.

All workers in America are entitled to pay into Social Security and based on their pay history, to receive a lifetime income each month starting from ages 62 to 70.
Ideally prior to retirement, you’ll also maximize other income sources that include taxable savings, IRAs, ROTH, Qualified plans (401K, 403b, 457b), annuities, deferred compensation, and employer pension plans.
Since your future Social Security benefit is calculated from your Social Security work history, you must ensure (and correct if necessary) that this history has been recorded correctly at www.socialsecurity.gov/myaccount OR the new www.ssa.gov/myaccount.
Social Security benefit calculation uses your top 35 highest earning years and projects your estimated benefit at your FULL RETIREMENT AGE (FRA).
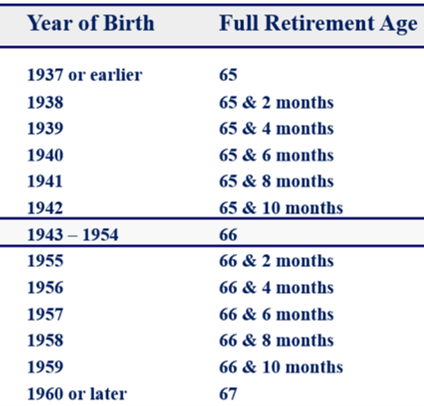
Your FRA is based on your birth year and, as you can see on this table, it has been increasing. In fact, since 1983 when the FRA was 65, it has been increased gradually so that by 2025 (for those born in 1960 or later) the FRA will be 67. To understand Social Security, you must first determine your FRA.
When can you collect Social Security? At FRA, you can file and receive your full benefit (100%) based on the amount of Social Security tax paid to your Social Security number. The earliest you can collect Social Security benefits on your record is at age 62 (when your FRA amount is reduced ½% for each month or 6% less each year until FRA) and the latest at age 70. If you delay past your FRA, you earn Delayed Retirement Credits (DRC) and for each month it will grow two-third of a percent or 8% per year until age 70.
Example of how benefits are calculated: If you were born in 1960 and your FRA amount is $1K/month then collecting at age 62 will result in a lifetime amount of $700/month but delaying until age 70 would result in $1,240/month (plus annual COLA adjustment).
When creating your financial plan, we will consider different Social Security timing strategies based on your financial and longevity expectations. When deciding on your best timing we always request that you consider your health, your family’s longevity, and known increases in population longevity.
Compared to what you earned, what can you expect to receive?
As an example, an average earner ($58K) could receive $1,907 or $23K per year in benefits for life, starting at FRA. On the other hand, those who paid Social Security at maximum earnings for 35 years would receive $3,822/month or $45K per year if 2022 was their FRA.
What if you take early benefits while still working? It seldom makes sense to work and take Social Security benefits early because your benefits are reduced by $1 for each $2 earned above an annually set earning level (in 2024 you can only earn up to $22,320 per year ($1,860/month) before your benefits are reduced). Once you reach FRA your Social Security benefits are NOT reduced (regardless of earnings).
We encourage each of you to work with us to review your Social Security history and then use your financial plan to make the best Social Security timing decision for you.
Applying for Social Security should be started three to four months prior to your chosen Social Security benefit start date. You would apply online at www.socialsecurity.gov or call (800-772-1213) or go to the local Social Security office.
One last and very important cyber security reminder: Protect your Social Security log in information (or credentials) – make certain that you are using a secure device when you log into your account.
Edi Alvarez, CFP®
BS, BEd, MS
